Cryptocurrency has evolved from a niche interest to a mainstream investment opportunity, attracting individuals from all walks of life. One of the key appeals of cryptocurrency is the potential for passive income, allowing investors to earn without actively managing their assets. Among the various ways to generate passive income in the crypto world, staking has emerged as one of the most popular strategies. But is staking really the best way to earn passive income in cryptocurrency? In this article, we will explore what staking is, how it works, its benefits, risks, and whether it is the optimal choice for earning passive income in the crypto space.
Key Takeaways
- Staking involves locking up cryptocurrency to help secure a blockchain network in exchange for rewards.
- It offers a higher return than traditional investments, but it carries risks like market volatility and lock-up periods.
- While staking can be an effective passive income strategy, it’s not suitable for everyone. Carefully consider your financial goals and risk appetite before staking.
- Always research the cryptocurrency and network you plan to stake on, and be mindful of potential fees and slashing risks.
| Method | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Staking | – Passive income generation – High potential returns (5%–20%) – Contributes to network security – Environmentally friendly compared to mining – Easy for beginners to participate | – Market volatility risk – Lock-up periods – Potential slashing penalties – Staking pool fees | Long-term investors Risk-averse individuals |
| Yield Farming | – High return potential (can exceed 20% or more) – Flexible (may involve liquidity provision) | – High risk and volatility – Complex process – Requires a deep understanding of DeFi protocols | Advanced users Risk-tolerant investors |
| Crypto Trading (Spot & Margin) | – High return potential – Active management can lead to significant gains – Flexibility to exit quickly | – Requires time, expertise, and constant monitoring – Can be very volatile – Emotional stress | Active traders Short-term investors |
| Mining (Proof of Work) | – Strong blockchain security – Passive income once hardware is set up – Can be very profitable (especially in bull markets) | – High initial investment in hardware – High energy consumption – Ongoing maintenance costs | Tech-savvy individuals Heavy capital investment |
| Staking Pools | – Lower technical barrier compared to solo staking – Pool operators manage staking rewards | – Pool fees – Less control over staking process – Risk of centralization in some pools | Beginners Investors looking for hands-off approach |
| Lending (Crypto Loans) | – Stable returns (5%–15%) – Lower risk compared to trading and yield farming – Can be done through exchanges or platforms | – Potential borrower defaults – Platform risks – Less flexibility (locked funds) | Conservative investors Low-risk tolerance |
What is Staking in Cryptocurrency?
Staking refers to the process of actively participating in the validation of transactions on a proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain network. Unlike proof-of-work (PoW) networks like Bitcoin, where miners use computational power to validate transactions, PoS-based networks rely on users who “stake” their own cryptocurrency to help secure the network. In return for staking their coins, participants are rewarded with additional cryptocurrency, often referred to as “staking rewards.”

For example, in the Ethereum 2.0 network, holders of Ether (ETH) can stake their coins to help maintain the network’s consensus. In return, they receive a portion of the transaction fees and newly minted ETH. Staking offers a way for crypto holders to put their assets to work while maintaining the security and integrity of the network.
How Does Staking Work?
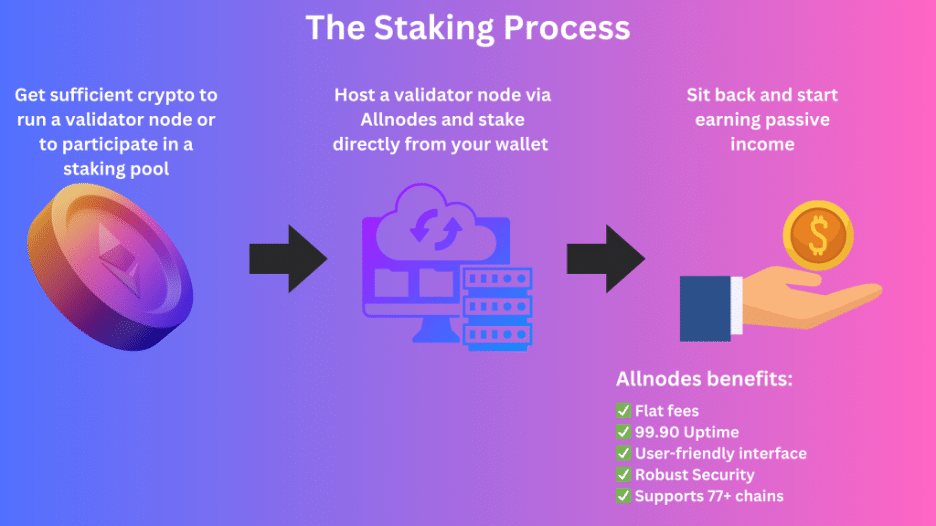
Staking operates on a consensus mechanism called Proof of Stake (PoS), which is an alternative to Proof of Work (PoW). In PoS, participants lock up a certain amount of their cryptocurrency to become validators. These validators help confirm transactions and secure the blockchain by creating new blocks. When a user stakes their crypto, they essentially agree to put their funds at risk, supporting the network and, in return, earning rewards based on the amount they’ve staked and the network’s success.
The process of staking typically involves the following steps:
- Choose a Cryptocurrency to Stake: Not all cryptocurrencies support staking. Popular options include Ethereum 2.0 (ETH), Cardano (ADA), Solana (SOL), and Polkadot (DOT). Before staking, research the coin’s staking rewards, lock-up periods, and network credibility.
- Select a Staking Method: You can stake through a cryptocurrency exchange, a staking pool, or independently by running your own validator node. Staking through exchanges is often the easiest method, as platforms like Binance and Coinbase allow users to stake their assets with minimal technical knowledge required.

- Stake Your Tokens: Once you’ve chosen a method, you can lock your crypto in a wallet or platform. After staking, you’ll begin receiving rewards, which typically accumulate over time.
- Earn Staking Rewards: Staking rewards are typically distributed in the form of the cryptocurrency you staked or a portion of transaction fees from the network. The reward rate depends on several factors, such as the number of participants, the amount of staked assets, and network inflation.
- Unstaking (Optional): Staked crypto can often be unstaked, but there may be lock-up periods and withdrawal fees depending on the network and method used. Some platforms allow you to withdraw staked funds at any time, while others have lock periods ranging from a few days to a year.
Benefits of Staking as a Passive Income Strategy
1. Passive Income Generation
The primary benefit of staking is the ability to earn passive income. When you stake your coins, you’re essentially putting them to work without having to actively trade or manage them. This makes staking an ideal strategy for long-term investors who want to earn rewards while holding onto their assets.
Staking offers a number of benefits that make it an attractive option for investors seeking passive income. Here are some key advantages:
2. High-Return Potential
Staking can offer higher returns than traditional investment vehicles like savings accounts or bonds. Depending on the network and your chosen method, staking rewards can range from 5% to 20% annually. This is a significant advantage over traditional passive income options, which often offer very low returns in comparison.
3. Contribution to Network Security
By staking, you are directly contributing to the security and operation of the blockchain network. Your staked assets help ensure that transactions are validated and that the network remains decentralized. In this sense, staking serves as both an investment and a contribution to the larger cryptocurrency ecosystem.
4. Diversification of Income Sources
Staking can complement other income-generating activities within the cryptocurrency ecosystem, such as trading or yield farming. By staking your crypto, you can diversify your income streams and increase the potential for growth in your overall portfolio.
5. Lower Energy Consumption
Compared to mining, staking is much more energy-efficient. While mining relies on powerful computing hardware to solve complex mathematical problems, staking uses much less energy, as it doesn’t require the same computational power. This makes it a more environmentally friendly option for earning passive income.
Risks and Challenges of Staking
While staking has its benefits, it’s important to understand that it’s not without risks. Some of the potential challenges and risks associated with staking include:
1. Market Volatility
Cryptocurrencies are notoriously volatile. While staking offers the potential for high rewards, the value of the staked tokens may fluctuate significantly, meaning you could lose money if the price of the asset decreases. This volatility is something that investors should carefully consider before committing to staking.
2. Lock-Up Periods
Many staking mechanisms require you to lock up your cryptocurrency for a specific period, during which time you cannot access or sell your assets. While this ensures that you contribute to network security, it can also prevent you from taking advantage of sudden market opportunities or addressing personal financial needs.

3. Slashing Risk
In some PoS networks, if a validator misbehaves or fails to properly validate transactions, they can be penalized by having a portion of their staked coins slashed. This means you could lose a part of your staked assets if you’re involved in a staking pool or act as a validator node.
4. Network Risk
Staking rewards depend heavily on the health and security of the network. If a network is compromised, or if the cryptocurrency experiences a significant decline in user activity or market confidence, the rewards you receive may decrease, or you could lose your staked assets altogether.
5. Staking Pool Fees
If you choose to stake via a pool or exchange, there may be fees associated with the service. While these fees are typically lower than the potential rewards, they can still eat into your profits. Always check the fees involved before committing your crypto to a staking platform.
Is Staking the Best Way to Earn Passive Income in Cryptocurrency?
While staking offers an attractive passive income opportunity, it’s important to recognize that it may not always be the best option for every investor. Factors such as your risk tolerance, investment strategy, and knowledge of the cryptocurrency market will determine whether staking is a suitable choice.

For investors who are risk-averse and prefer a more hands-off approach, staking can offer stable, predictable returns, especially in established networks like Ethereum, Cardano, or Polkadot. However, for those who are more risk-tolerant and willing to engage in more active management of their portfolios, other options like trading or yield farming may provide higher returns.
Also Read : What Is a DeFi Wallet and How Does It Work?
Conclusion
Staking is undoubtedly one of the most attractive ways to earn passive income in the cryptocurrency world. With the potential for high rewards, a relatively simple process, and low energy consumption compared to mining, staking presents a strong case for those looking to make their crypto holdings work for them. However, like all investments, it’s important to weigh the risks involved, particularly market volatility, lock-up periods, and network-specific issues. Whether staking is the best passive income strategy depends on your individual risk tolerance, knowledge, and goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the minimum amount of cryptocurrency I need to stake?
The minimum amount required to stake varies by cryptocurrency. Some networks allow as little as 1 coin, while others, like Ethereum 2.0, require a minimum of 32 ETH to run your own validator node.
How long do I have to lock up my crypto in staking?
The lock-up period varies between different blockchain networks and staking platforms. Some networks have flexible withdrawal options, while others may have lock-up periods ranging from a few days to a year.
Can I unstake my crypto anytime?
Many networks allow you to unstake your assets, but some may have a waiting period before you can withdraw your funds. It’s important to check the specific conditions of the platform or network you’re staking with.
Are staking rewards taxable?
Yes, staking rewards are considered taxable income in most jurisdictions. It’s important to consult with a tax professional to understand how staking income is taxed in your country.
What happens if the network I’m staking on gets hacked?
If the network you’re staking on experiences a hack or security breach, your staked assets could be at risk. Always do thorough research on the security measures of the network before staking.
Can I stake any cryptocurrency?
Not all cryptocurrencies support staking. Only those that operate on a Proof of Stake (PoS) or similar consensus mechanism allow staking. Make sure the coin you’re interested in supports staking before committing.
Do I need special hardware to stake my crypto?
If you’re staking through an exchange or staking pool, you typically don’t need special hardware. However, if you want to become a validator and stake independently, you may need to run your own node, which requires some technical knowledge and hardware.

