In an increasingly digital world, the way we handle money and transactions is evolving rapidly. One such innovation is the digital wallet, a tool that allows users to store and manage their payment information electronically. Digital wallets have revolutionized the way we make payments, enhancing convenience, security, and accessibility. Whether for mobile payments, online shopping, or cryptocurrency transactions, digital wallets are becoming an integral part of our everyday financial activities.
In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about digital wallets, how they work, their types, benefits, and frequently asked questions.
Key Takeaways
| Key Feature | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Convenience | Digital wallets streamline the payment process, allowing quick transactions. |
| Enhanced Security | They use encryption and tokenization to protect user data. |
| Transaction Fees | Digital wallets often reduce transaction fees compared to traditional methods. |
| Contactless Payments | NFC technology allows tap-and-go payments, eliminating the need for physical cards. |
| Managing Multiple Payments | You can store several payment methods in a single wallet. |
| Loyalty Programs | Digital wallets support storing and redeeming loyalty points and rewards. |
| Challenges | Security concerns and limited acceptance in some regions are challenges to consider. |
What is a Digital Wallet?
A digital wallet (also known as an e-wallet) is a software application or an online service that allows users to store and manage their payment information, such as credit and debit card details, and make payments electronically. It eliminates the need to carry physical wallets with paper money or cards and allows users to securely pay for goods and services using their smartphones, computers, or other connected devices.
Digital wallets can hold various forms of payment, including:
- Credit and Debit Cards
- Cryptocurrency
- Gift Cards
- Loyalty Points
- Cash Balances
How Does a Digital Wallet Work?
Digital wallets work by storing a user’s payment information securely on a smartphone, computer, or cloud-based service. When you make a payment or transfer money, the digital wallet interacts with the payment processor to verify and authorize the transaction.
Here’s a breakdown of how digital wallets function:
Step 1: Adding Payment Information
Users typically add their payment methods to the digital wallet by entering details like credit card numbers, bank account details, or cryptocurrency wallets. This information is securely encrypted and stored.
Step 2: Authentication
For security purposes, users may need to authenticate themselves using PIN codes, biometric identifiers (such as fingerprints or facial recognition), or other multi-factor authentication methods before authorizing transactions.
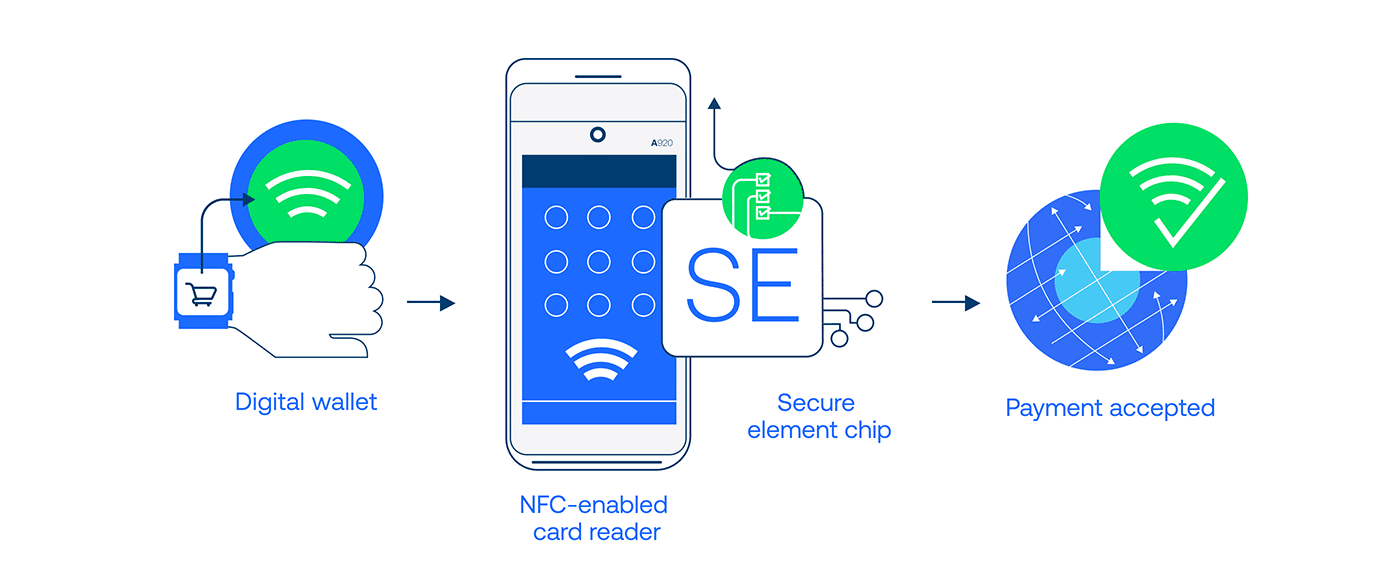
Step 3: Making Payments
When making a purchase, the digital wallet uses Near Field Communication (NFC) technology or QR codes for contactless payments. For online shopping, digital wallets can autofill your payment details, making the checkout process faster and more efficient.
Step 4: Transaction Confirmation
Once the payment is made, the wallet notifies the user of the transaction’s status. The system ensures that the user has sufficient funds or credit to complete the transaction.
Types of Digital Wallets
There are various types of digital wallets, each serving different needs and purposes. Here are the most common categories:
1. Closed Digital Wallets
Closed wallets are issued by specific merchants or service providers. They can only be used within the issuer’s network, making them highly restricted. For example, a store-specific digital wallet might only allow you to make purchases from that store or redeem loyalty points.
2. Semi-Closed Digital Wallets
Semi-closed wallets offer greater flexibility than closed wallets but still restrict the user to a specific network. These wallets can be used to make purchases with specific merchants or service providers who are part of the wallet’s network. PayPal is a widely known example, as it can be used across multiple online platforms but only with partners that accept PayPal.
3. Open Digital Wallets
Open digital wallets are the most flexible type. These wallets allow users to perform a wide range of transactions, from making purchases and transferring money to others, to paying bills and withdrawing cash from ATMs. Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay are popular examples of open wallets.
4. Cryptocurrency Wallets
Cryptocurrency wallets are used to store digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other altcoins. These wallets can be either hot wallets (online) or cold wallets (offline storage devices). Cryptocurrency wallets enable users to send, receive, and store digital assets securely.
Benefits of Digital Wallets
Digital wallets offer numerous advantages, which is why they are gaining popularity among users worldwide.
1. Convenience
One of the key benefits of digital wallets is convenience. Users no longer need to carry physical credit cards, cash, or loyalty cards. Everything is stored in one place, accessible at any time, which makes online and in-store payments quick and easy.
2. Enhanced Security
Digital wallets use encryption and tokenization to protect user data. When a payment is made, digital wallets often don’t share your actual credit card number. Instead, they use a one-time token or a virtual card number, making it difficult for hackers to steal your financial information.
3. Reduced Transaction Fees
Digital wallets often eliminate the need for traditional intermediaries like banks, leading to lower transaction fees. This is especially beneficial for international money transfers.
4. Contactless Payments
Many digital wallets use NFC technology to enable contactless payments. This allows users to simply tap their phone or smart device on a payment terminal to complete transactions without the need to physically swipe or insert a card.
5. Managing Multiple Payment Methods
Digital wallets allow users to store multiple payment methods, including credit and debit cards, gift cards, and cryptocurrency wallets, making it easier to manage finances and switch between payment methods as needed.
6. Loyalty and Rewards Programs
Many digital wallets integrate loyalty programs, allowing users to store and redeem points, rewards, or discounts directly from the wallet, providing a more streamlined shopping experience.
Challenges of Digital Wallets
Despite their many benefits, digital wallets also face challenges that users need to consider.
1. Security Concerns
Although digital wallets offer enhanced security, they are not immune to cyber threats. Users must remain vigilant to prevent theft of their credentials or wallet access through phishing attacks, malware, and other forms of cybercrime.
2. Limited Acceptance
While the adoption of digital wallets is growing, not all merchants accept digital wallets as a payment method. In some regions, especially in developing countries, digital wallets are less widely accepted than traditional payment methods.
3. Technical Issues
Digital wallets are dependent on technology and connectivity. Server outages, software glitches, or device compatibility issues can disrupt access to funds and hinder payments.
4. Loss of Access
If a user loses access to their digital wallet, either due to password loss, phone theft, or other issues, regaining access can be difficult. Although recovery methods exist, they are often time-consuming and require verification.
Certainly! Here’s the refined content without any lines:
Types of Digital Wallets
Understanding the Different Wallets in Detail:
- Closed Wallets: These are issued by specific merchants or brands and can only be used within their network. For example, a store-specific wallet such as Starbucks Wallet allows customers to purchase coffee or accessories only within their own retail chain.
- Semi-Closed Wallets: These wallets can be used across multiple merchants within a predefined network. Examples include Paytm, which can be used at various merchants, but only those partnered with the service.
- Open Wallets: Open digital wallets, such as Google Pay and Apple Pay, are designed for broad usage. These wallets allow users to make payments at a wide variety of stores, withdraw money from ATMs, and more.
- Cryptocurrency Wallets: These wallets store digital currencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, or Litecoin. Cryptocurrency wallets can be hot wallets (internet-connected) or cold wallets (offline storage for added security).
- Hybrid Wallets: A combination of a closed and open wallet, allowing users to store both physical and digital assets like loyalty points, digital currency, and traditional payment methods.
How Digital Wallets Enhance E-commerce
Impact on Online Shopping and Transactions:
- Faster Transactions: Digital wallets streamline the online checkout process by auto-filling payment information, reducing the time spent inputting credit card details.
- Global Accessibility: As digital wallets can process payments internationally, they make cross-border shopping and transactions more convenient and less costly for both buyers and sellers.
- Convenience for Subscription Services: Digital wallets are often used to facilitate payments for subscription-based services like Netflix, Spotify, and Amazon, providing automatic, recurring billing.
- Integration with Retailers’ Websites: Many e-commerce platforms integrate digital wallet options such as PayPal, Apple Pay, or Google Pay, making it easier for users to make purchases without switching between apps.
Blockchain Integration with Digital Wallets
How Blockchain is Powering Secure Digital Wallets:
- Cryptocurrency Transactions: Blockchain-based wallets are designed to store digital currencies securely. Bitcoin wallets, for example, rely on the underlying blockchain to enable secure peer-to-peer transactions.
- Improved Security Protocols: Blockchain wallets leverage private keys and public keys to ensure secure transactions. The decentralized nature of blockchain provides protection against centralized server hacks.
- Smart Contract Integration: Blockchain-based wallets can integrate with smart contracts for automated transactions in areas like DeFi (Decentralized Finance) and NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), where transactions are automatically executed when certain conditions are met.
- Immutable Record Keeping: Blockchain provides a transparent ledger that records transactions in a way that cannot be altered or tampered with, ensuring all financial transactions are traceable and verifiable.
NFC Technology in Digital Wallets
Near Field Communication (NFC) and its Role in Digital Payments:
- What is NFC? NFC technology allows two devices (such as a smartphone and a payment terminal) to communicate wirelessly within close proximity, typically less than 4 centimeters.
- Contactless Payments: Using NFC, digital wallets enable contactless payments at retailers, allowing customers to simply tap their smartphone or smartwatch on a point-of-sale (POS) terminal.
- Security Features: NFC payments are considered secure because the encrypted data is transmitted between devices in an almost instantaneous manner, making it harder for fraudsters to intercept.
- Widespread Adoption: NFC is gaining popularity across global markets. Countries such as the UK, the US, and Australia have integrated NFC technology into both their banking system and retail infrastructure, making it common to use mobile wallets for everyday purchases.
Digital Wallets for Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Transactions
How Digital Wallets Facilitate Quick Money Transfers Between Individuals:
- P2P Payment Systems: Digital wallets enable instant money transfers between individuals. Services like Venmo, Zelle, and Cash App make it easy to transfer money between bank accounts or wallets without the need for a third-party intermediary.
- Mobile Payments in Social Media: Social media platforms such as Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp are now integrated with P2P payment systems, allowing users to send money directly through chat applications.
- International P2P Payments: Services like PayPal and Wise (formerly TransferWise) allow for international peer-to-peer payments with lower fees and better exchange rates than traditional banking systems.
Digital Wallets and Cryptocurrency
Exploring the Intersection of Cryptocurrency and Digital Wallets:
- Hot Wallets vs. Cold Wallets: Hot wallets are internet-connected, making them convenient for quick transactions but more vulnerable to online attacks. Cold wallets, on the other hand, store private keys offline, providing better protection for long-term storage.
- Storing Cryptocurrencies Safely: Popular cryptocurrency wallets like Coinbase Wallet, MetaMask, and Trust Wallet allow users to securely store their private keys and digital assets.
- Multi-Currency Support: Many digital wallets, such as Exodus, support the storage of multiple cryptocurrencies, allowing users to manage a diversified crypto portfolio in one place.
- Wallet Security Features: Strong encryption, two-factor authentication (2FA), and biometric identification are standard security measures used in digital cryptocurrency wallets to protect against unauthorized access.
The Future of Digital Wallets and Financial Technology
How Emerging Technologies are Shaping the Future of Digital Wallets:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can personalize user experience by suggesting payment options based on past transactions or analyzing spending habits. AI-driven fraud detection algorithms also provide advanced security to prevent unauthorized transactions.
- Blockchain 2.0 and Smart Wallets: The development of next-gen blockchains and smart contract-enabled wallets could allow users to automate financial management tasks and access a wider range of decentralized financial services.
- Integration with IoT (Internet of Things): As more everyday devices become connected (e.g., smart refrigerators, watches, cars), digital wallets could seamlessly enable automatic payments for purchases made through these devices.
- Biometric Authentication: Future wallets may rely on more advanced biometric authentication methods (like iris scanning or voice recognition) for verifying identity, making it harder for fraudsters to access personal funds.
- CBDCs (Central Bank Digital Currencies): The rise of centralized digital currencies, such as China’s Digital Yuan, could integrate into digital wallets to give users the ability to transact directly with government-issued digital money.
Digital Wallets and Their Impact on Traditional Banking
How Digital Wallets are Disrupting the Banking Industry:
- Banking without a Bank: With the advent of mobile wallets like Revolut and Monzo, users no longer need traditional bank accounts to make payments, transfer money, or store funds. These digital-first platforms operate without brick-and-mortar branches.
- Cross-Border Payments: Digital wallets eliminate the need for intermediary financial institutions by providing low-cost international money transfers. Services like PayPal and Wise allow users to send funds to recipients in different countries with reduced exchange fees.
- Financial Inclusion: Digital wallets provide banking access to people in underbanked and unbanked populations, offering them a secure, accessible way to store and transfer funds without traditional banking infrastructure.
Regulatory Landscape of Digital Wallets
Navigating Legal, Compliance, and Privacy Concerns:
- Regulations for Cryptocurrency Wallets: Many countries are establishing regulatory frameworks for the use of digital currencies and the wallets that store them. These include anti-money laundering (AML) laws and know your customer (KYC) requirements.
- Data Privacy Concerns: The storage of payment data and personal information in digital wallets raises significant privacy concerns. The GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe sets stringent rules on how companies collect, process, and store user data.
- Consumer Protection Laws: With the increase in digital wallet adoption, governments are introducing regulations to protect consumers from fraud, unauthorized transactions, and loss of funds in digital wallets.
Best Practices for Securing Digital Wallets
Tips to Keep Your Digital Wallet Safe and Secure:
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Always activate multi-factor authentication on your wallet for an added layer of security.
- Use Strong Passwords: Create complex, unique passwords for your wallet account and change them regularly.
- Avoid Public Wi-Fi for Transactions: Avoid using unsecured networks when accessing your wallet, as this increases the risk of hacking.
- Backup Your Wallet: Many digital wallets offer a backup feature that lets you store your data securely offline, such as writing down recovery phrases or using cloud-based backup services.
- Regularly Monitor Transactions: Keep an eye on your wallet’s activity and immediately report any suspicious transactions.
Read More : What Are Nodes and How Do They Work?
Conclusion
Digital wallets are transforming the way we manage money and make payments, offering unparalleled convenience, enhanced security, and flexibility. Whether you’re shopping online, transferring money, or storing cryptocurrencies, digital wallets provide a secure, efficient, and modern way to handle your finances. However, as with any technology, users must remain cautious about security risks and ensure they use wallets that fit their needs.
FAQs
1. How secure is a digital wallet?
Digital wallets use encryption and tokenization to ensure the security of user data. However, users must also practice good security habits, such as enabling two-factor authentication and avoiding phishing scams.
2. Can I use my digital wallet internationally?
Yes, many digital wallets, like PayPal and Google Pay, allow international transactions. However, some wallets may have regional restrictions or incur additional fees for cross-border payments.
3. Do I need an internet connection to use a digital wallet?
You typically need an internet connection to access your wallet and complete transactions. However, some wallets (especially cryptocurrency wallets) allow offline access for certain functions.
4. Can I store cryptocurrency in a digital wallet?
Yes, digital wallets specifically designed for cryptocurrencies can store digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others. These wallets can be either hot (online) or cold (offline) storage.
5. Is a digital wallet the same as a mobile payment system?
While there is some overlap, digital wallets are broader in functionality. They not only allow mobile payments but can also store gift cards, loyalty points, and even cryptocurrencies, whereas mobile payment systems primarily focus on facilitating payments.
6. Can I link my bank account to a digital wallet?
Yes, most digital wallets allow you to link a bank account or credit/debit card to your wallet to make payments or transfer money. Examples include linking a bank account to PayPal or adding a credit card to Apple Pay.
7. Are there fees for using a digital wallet?
Digital wallets may charge fees for certain transactions, such as currency conversion, international transfers, or adding funds. Fees vary depending on the wallet provider and the type of transaction.