Blockchain technology is a transformative innovation that has reshaped how data is handled, stored, and transferred across various industries. Originally conceived as the underlying technology for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain has evolved beyond its financial roots, now being utilized in fields ranging from healthcare and supply chains to government and entertainment. But what exactly is blockchain, how does it work, and why is it considered revolutionary?
In this article, we’ll explore the fundamental aspects of blockchain technology, including its definition, structure, working mechanism, advantages, and challenges. We’ll also answer common questions about its applications and future potential.
Key Takeaways
- Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that ensures security, transparency, and immutability.
- It has applications in various fields beyond cryptocurrencies, including supply chains, healthcare, and voting systems.
- While blockchain offers many advantages, it also faces challenges such as scalability issues and regulatory uncertainty.
- The future of blockchain looks promising, with ongoing developments aimed at improving its scalability, security, and energy efficiency.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across many computers in such a way that the registered transactions cannot be altered retroactively. This ensures a level of transparency, security, and reliability that traditional centralized systems cannot provide.
The word “blockchain” comes from its structure. A blockchain is essentially a chain of blocks, where each block contains a set of transactions. Each block is linked to the previous one via cryptographic hashes, making it virtually impossible to tamper with past data without altering all subsequent blocks—something that is computationally infeasible in large blockchain networks.
How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
At its core, blockchain operates as a distributed ledger that allows for secure and transparent peer-to-peer transactions without needing a central authority or intermediary. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how blockchain works:
1. Transaction Initiation
A user initiates a transaction by creating a request. This request could involve transferring cryptocurrency, executing a smart contract, or recording other types of data.
2. Transaction Validation
Before the transaction can be added to the blockchain, it must be validated. This is done through a consensus mechanism, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). The validators (also called miners or nodes) ensure that the transaction is legitimate and adheres to the rules of the network.
3. Transaction is Recorded in a Block
Once validated, the transaction is bundled with others into a block. This block is then broadcast to the network.
4. Block is Added to the Chain
Once consensus is reached, the block is added to the existing blockchain. The newly added block is linked to the previous block using a cryptographic hash, forming a chain. This makes it tamper-resistant because altering any block would require recalculating every subsequent block.
5. Transaction Confirmation
The transaction is now confirmed and can’t be changed without the agreement of the majority of the network, providing a high level of security.
What Are the Key Features of Blockchain?
Decentralization
Unlike traditional centralized systems where a single entity (e.g., a bank) controls the system, blockchain is decentralized. This means that no single party has complete control over the network, which reduces the risk of fraud or manipulation.
Transparency
Blockchain transactions are publicly available on the network and can be viewed by anyone. This transparency ensures accountability and builds trust among users.
Security
Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to ensure that data is secure and tamper-proof. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it is extremely difficult to alter.
Immutability
The immutability of blockchain is one of its key advantages. Once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted. This ensures that records remain intact over time.
Efficiency
Blockchain can streamline processes by eliminating intermediaries and reducing transaction times. This is particularly useful in industries like finance, where transactions can take several days due to intermediaries.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Cryptocurrencies
The most famous application of blockchain technology is cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Blockchain allows secure, transparent, and decentralized digital currency transactions without the need for traditional financial intermediaries.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology enhances transparency in supply chains by providing a secure, immutable record of every transaction and movement of goods. This can reduce fraud, increase traceability, and improve efficiency in supply chains across various industries.
Healthcare
Blockchain is increasingly used in healthcare to securely store patient records and ensure that they are accessible only to authorized individuals. It also enables healthcare professionals to access accurate and up-to-date medical information.
Smart Contracts
A smart contract is a self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automatically execute and enforce themselves when certain predefined conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries and minimizing the risk of errors.
Voting Systems
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way elections are conducted by providing secure, transparent, and tamper-proof voting systems that reduce the risk of fraud and increase voter participation.
Digital Identity
Blockchain can provide a secure, decentralized way for individuals to manage their digital identities, ensuring privacy and preventing identity theft.
What Are the Advantages of Blockchain
- Enhanced Security: Blockchain’s decentralized nature and cryptographic methods make it more secure than traditional systems.
- Reduced Costs: By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain can significantly reduce transaction and operational costs.
- Increased Transparency: Blockchain allows for transparent and auditable transactions that can be traced in real-time.
- Faster Transactions: Blockchain transactions, particularly in cryptocurrency and cross-border payments, can be processed faster than traditional banking systems.
- Immutability and Integrity: Once recorded, data in a blockchain cannot be altered, ensuring data integrity.
What Are the Challenges of Blockchain?
While blockchain technology offers numerous benefits, it also comes with its challenges:
Scalability Issues
Blockchain networks, particularly those based on Proof of Work (PoW), often face scalability issues due to the need for complex computational work. As more transactions are added to the network, the processing time can increase, leading to slower transactions.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Blockchain’s decentralized nature presents challenges for regulators, particularly in industries like finance and healthcare. Governments around the world are still grappling with how to regulate blockchain-based assets like cryptocurrencies.
Energy Consumption
Blockchain technologies like Bitcoin’s Proof of Work require significant amounts of energy to mine new blocks, raising concerns about their environmental impact.
Adoption Barriers
Despite its advantages, many industries are still hesitant to adopt blockchain due to the complexity of integrating it with existing systems and the cost of implementing it.
Sure! Here’s the modified version with h2 titles and no numbers:
Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms: How They Secure the Network
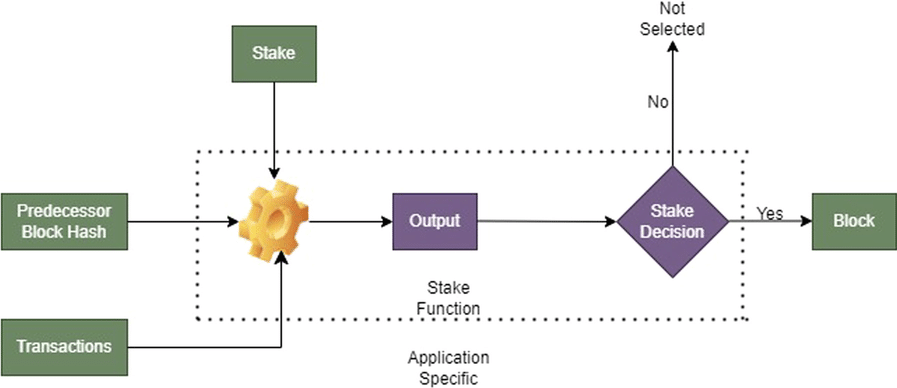
Overview:
- Consensus mechanisms are essential to the operation of any blockchain network. These algorithms allow decentralized nodes to reach an agreement on the validity of transactions.
- The most common consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and more recent models like Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT).
Key Points to Explore:
- Proof of Work (PoW): How it works, its energy consumption, and its use in Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): How it differs from PoW and its energy efficiency.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): How voting systems are used to improve scalability.
- Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT): Its application in permissioned blockchains.
Why This Is Important:
- Each consensus mechanism impacts the security, scalability, and efficiency of the blockchain network. This topic is key to understanding how blockchain networks achieve trust without central authority.
Smart Contracts: Revolutionizing Business with Code
Overview:
- Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into lines of code. They automate contract execution when predefined conditions are met.
- Smart contracts can be applied across industries, including finance (for loans), insurance (automated claims), and real estate (property transfer).
Key Points to Explore:
- How Smart Contracts Work: The technical execution of smart contracts on blockchains such as Ethereum.
- Benefits: Reduced need for intermediaries, enhanced security, and lower transaction costs.
- Challenges: Coding errors, legal challenges, and enforceability in real-world contexts.
- Real-World Examples: Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms like MakerDAO and Compound.
Why This Is Important:
- Smart contracts can transform how businesses and industries operate, creating efficiencies and reducing human error. However, legal implications and technical flaws remain areas of concern.
Blockchain in Supply Chain Management: A New Era of Transparency
Overview:
- Blockchain offers a way to track every step in the supply chain, ensuring transparency, authenticity, and efficiency. Companies are using blockchain to trace the journey of products from the point of manufacture to the end consumer.
Key Points to Explore:
- Tracking Provenance: How blockchain helps verify the authenticity of goods (e.g., food safety, luxury goods, pharmaceuticals).
- Reducing Fraud: Blockchain’s ability to minimize fraud and counterfeit goods.
- Examples of Adoption: Companies like IBM (Food Trust) and Walmart using blockchain for supply chain tracking.
- Efficiency Gains: How blockchain reduces paperwork and improves logistics management.
Why This Is Important:
- The ability to track products accurately across supply chains can revolutionize industries from food to pharmaceuticals, creating higher standards for transparency and consumer trust.
Blockchain and Healthcare: Securing Patient Data and Medical Records
Overview:
- Blockchain can revolutionize healthcare by providing secure, decentralized storage for medical records. Patients control access to their own data, ensuring that only authorized entities have access to sensitive information.
Key Points to Explore:
- Patient Data Privacy: How blockchain ensures that medical data remains private and accessible only by the right parties.
- Interoperability: Blockchain can facilitate seamless exchange of medical records between healthcare providers, enhancing collaboration.
- Case Studies: Projects like MedRec that aim to provide a decentralized solution for medical record management.
Why This Is Important:
- Healthcare data breaches are a significant concern, and blockchain’s ability to secure and control patient data could improve both privacy and the efficiency of healthcare systems worldwide.
Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence (AI): Synergy for the Future
Overview:
- The integration of blockchain and AI promises to deliver both improved decision-making and enhanced security in digital systems. While AI can automate processes and analyze data, blockchain can provide transparent, verifiable data storage.
Key Points to Explore:
- Blockchain for AI Data Integrity: How blockchain can ensure the quality and traceability of data used by AI algorithms.
- Decentralized AI: Blockchain can be used to build decentralized AI systems, where machine learning models and data are shared across a network without central control.
- Autonomous Systems: How blockchain can be used in autonomous vehicles and robots, offering decentralized trust for real-time decision-making.
Why This Is Important:
- Combining the decentralized, immutable nature of blockchain with the automation and data analysis power of AI could lead to new solutions for industries like finance, healthcare, and autonomous systems.
NFTs and Blockchain: Understanding the Digital Ownership Revolution

Overview:
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) represent ownership of unique digital assets such as art, music, videos, and virtual goods. These tokens are stored on a blockchain, which certifies their uniqueness and provenance.
Key Points to Explore:
- What Are NFTs?: Understanding how NFTs work and why they are unique compared to cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
- Applications of NFTs: Digital art, music royalties, collectibles, and gaming.
- NFT Marketplaces: Platforms like OpenSea, Rarible, and SuperRare that allow users to buy, sell, and trade NFTs.
- Environmental Concerns: How NFTs can impact the environment due to blockchain energy consumption.
Why This Is Important:
- NFTs are rapidly transforming industries like art, entertainment, and gaming by creating new ways to monetize digital assets. Their rapid rise has also sparked debates over copyright, value, and sustainability.
Blockchain in Government and Public Sector: Transforming Transparency and Voting Systems
Overview:
- Governments are exploring blockchain for a variety of applications, from improving the transparency of public services to revolutionizing voting systems and identity management.
Key Points to Explore:
- Digital Identity Verification: How blockchain can be used to create secure digital identities for citizens.
- Transparent Governance: Blockchain allows governments to make public records, contracts, and budgets fully transparent.
- Blockchain Voting: A secure, transparent system for voting that could eliminate fraud and ensure fairness.
- Case Studies: The Estonia e-Residency program and other blockchain-based initiatives for governance.
Why This Is Important:
- Blockchain has the potential to reshape governance by making processes more transparent and secure, reducing corruption, and improving public sector efficiency.
Blockchain for Cross-Border Payments: Speeding up Global Transactions
Overview:
- Blockchain can significantly reduce the time and cost of cross-border payments. Traditional international money transfers often take days and are costly, but blockchain-powered cryptocurrencies enable almost instant transfers at a fraction of the cost.
Key Points to Explore:
- How Blockchain Enhances Payment Speed: Instantaneous, direct transfers between individuals or organizations globally.
- Cryptocurrency Remittances: How blockchain-powered cryptocurrencies like Ripple (XRP) are changing remittance systems.
- Regulatory Challenges: Navigating the complexities of cross-border payments in the face of different regulations across countries.
Why This Is Important:
- Blockchain has the potential to transform global financial systems, making cross-border payments faster, cheaper, and more accessible, especially for underbanked populations.
The Environmental Impact of Blockchain: Solutions for Sustainability
Overview:
- One of the key criticisms of blockchain, particularly Proof of Work-based systems like Bitcoin, is its significant environmental impact due to the high energy consumption required for mining.
Key Points to Explore:
- Energy Usage in Blockchain: How Proof of Work and Proof of Stake impact energy consumption.
- Sustainable Blockchain Models: How blockchain projects like Ethereum are transitioning to more energy-efficient models (e.g., PoS).
- Carbon Footprint of Mining: The environmental consequences of large-scale mining operations.
- Green Blockchain Solutions: Projects aimed at making blockchain more environmentally friendly, such as carbon offset initiatives.
Why This Is Important:
- Addressing the environmental concerns of blockchain is crucial for its long-term adoption. Sustainable blockchain technologies are needed to balance the advantages of decentralization with ecological responsibility.
The Future of Blockchain Technology: Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
Overview:
- As blockchain continues to evolve, it’s essential to understand the future trends, challenges, and opportunities that will shape its development.
Key Points to Explore:
- Interoperability: The need for different blockchains to communicate with each other.
- Privacy and Security: The ongoing need to balance transparency with privacy protection.
- Blockchain for Enterprise: How businesses are using blockchain for supply chain management, fraud prevention, and data security.
- Regulatory Landscape: How governments will regulate Blockchain and cryptocurrencies in the coming years.
Why This Is Important:
- Understanding the future trends in blockchain technology helps businesses, developers, and policymakers make informed decisions about adoption, regulation, and investment in blockchain.
Also Read : What Is Social Media Optimization And How Can It Boost Your Online Presence?
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize numerous industries by offering a secure, transparent, and decentralized alternative to traditional systems. While it is still in its early stages, its benefits in terms of security, cost savings, and transparency are already being recognized across various sectors. However, scalability issues, regulatory challenges, and energy consumption concerns remain hurdles that need to be addressed for broader adoption.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between blockchain and Bitcoin?
Blockchain is the technology that powers cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. While Bitcoin is a specific cryptocurrency, blockchain is the underlying technology that allows Bitcoin to function in a secure, decentralized manner.
2. Can blockchain be hacked?
While blockchain is highly secure due to its decentralized nature and cryptographic algorithms, it is not entirely immune to attacks. Vulnerabilities can exist in the code of specific blockchain applications or through 51% attacks.
3. What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically execute and enforce themselves when the predefined conditions are met, without the need for intermediaries.
4. What is a decentralized ledger?
A decentralized ledger is a database that is shared and synchronized across multiple participants in a network. It is not controlled by a single central authority and is often used in blockchain systems.
5. How is blockchain used in supply chain management?
Blockchain enhances transparency and traceability in supply chains by providing an immutable record of transactions. It helps in tracking the movement of goods and verifying the authenticity of products.
6. What is Proof of Work (PoW)?
Proof of Work is a consensus mechanism used in blockchain networks like Bitcoin, where miners solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain.
7. Is blockchain only for cryptocurrencies?
No, blockchain has many other applications beyond cryptocurrencies, including healthcare, supply chain management, digital identity, and more.

